News
Monoclonal antibody VSB16 Step to a New Preclinical Stage
2018-01-01
Vivasolis had successful validated three potential mono-antibody hybridoma candidates including the VSB16.
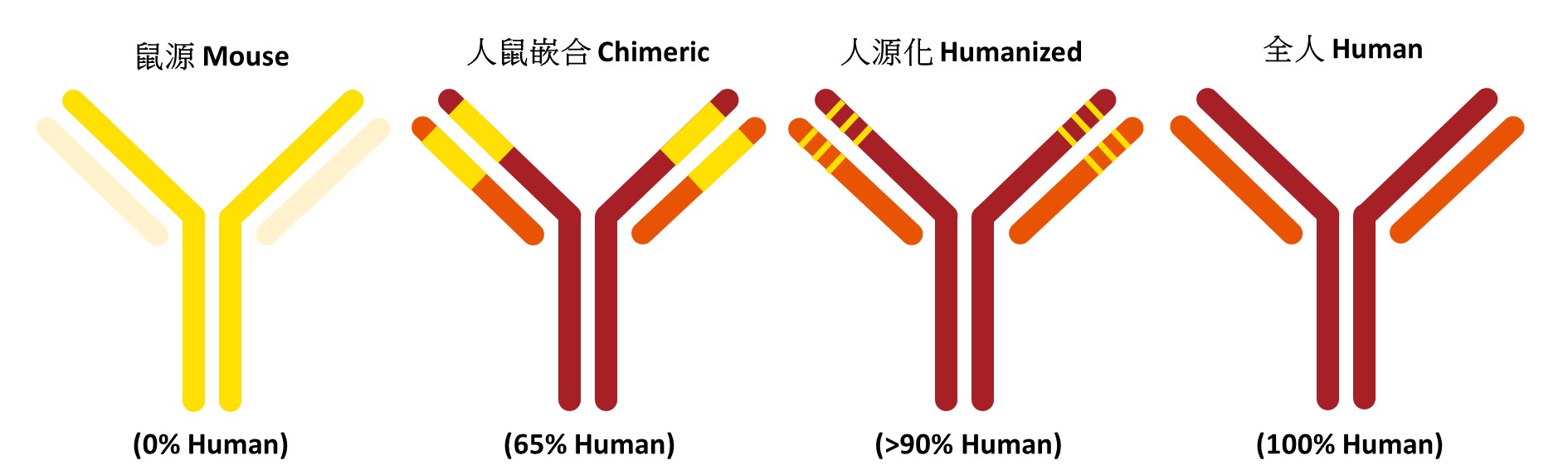
According to different immunogenicity, therapeutic antibody can be divided into four stages, consisting of murine antibody, chimeric antibody, humanized antibody and fully human antibody.
-Murine antibody
Initially, mouse antibodies are usually obtained by hybridoma technique, which is developed by fusing immortal mouse myeloma cells and splenic B cells from immunized animals. Murine antibody treatment leading to serious human anti-mouse antibody expression (HAMA reaction) which is an allergic reaction to the mouse antibodies that can range from a mild form to a more extreme and life-threatening response. HAMA reaction can also decrease the effectiveness of the treatment.
-Chimeric antibody
The second generation of therapeutic antibody is chimeric antibody. Mouse antibody variable region gene and human antibody constant region gene were joined using recombinant DNA technology. The constructed chimeric vector was transfected into mouse myeloma cells and the cells expressed chimeric antibodies. Chimeric antibody improved the monoclonal antibody humanization proportion to about 70% are less likely to trigger an immune response than the murine monoclonal antibodies.
-Humanized antibody
In order to further improve humanization proportion, researchers provided a method for reducing immunogenicity brought by grafting of the CDRs (complementarity-determining region) from a mouse antibody onto a human variable region framework, creating humanized antibodies. Humanized therapeutic antibody improved humanization proportion to 85%-90%. Chimeric antibody and humanized antibody are main formats of human therapeutic antibody and play an important role in cancer therapy.
-Fully Human antibody
Another stage of therapeutic antibody is fully human antibody which benefits from the development of two technologies, (1)phage display and (2)transgenic mouse platforms. (1)Constant regions that are engineered by phage display technology. The phage display facilitates selection of a fully human antibody specific for a specific antigen improve the binding affinity.(2) By introducing human immunoglobulin loci into the mouse germlines with inactivated endogenous antibody machinery, the transgenic mouse strains can directly generate high affinity, fully human antibodies.
Vivasolis had successfully humanized the monoclonal antibody product VSB16.